Re: What is Trend line?
What Is a Trendline?
Trendlines are easily recognizable lines that traders draw on charts to connect a series of prices together or show some data's best fit. The resulting line is then used to give the trader a good idea of the direction in which an investment's value might move.
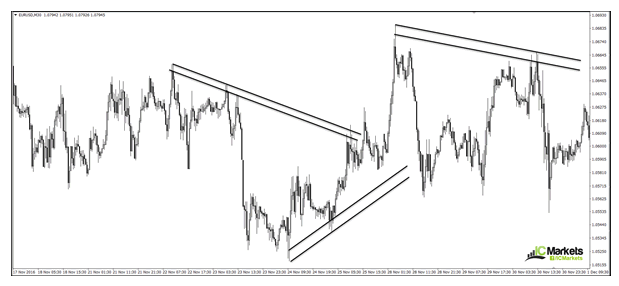
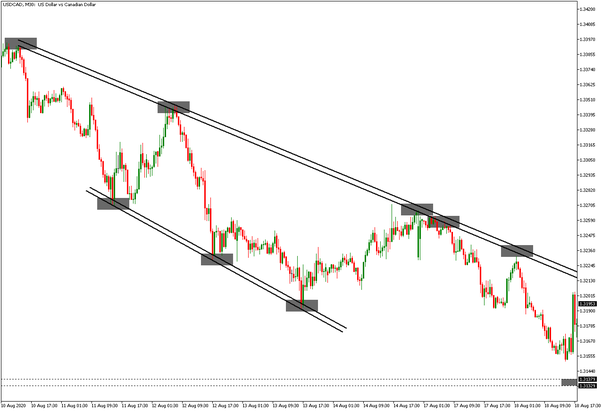
A trendline is a line drawn over pivot highs or under pivot lows to show the prevailing direction of price. Trendlines are a visual representation of support and resistance in any time frame. They show direction and speed of price, and also describe patterns during periods of price contraction.
Example Using a Trendline
Trendlines are relatively easy to use. A trader simply has to chart the price data normally, using open, close, high and low. Below is data for the Russell 2000 in a candlestick chart with the trendline applied to three session lows over a two month period.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dotdash_Final_Trendline_Nov_2020-01-53566150cb3345a997d9c2d2ef32b5bd.jpg)
The trendline shows the uptrend in the Russell 2000 and can be thought of as support when entering a position. In this case, trader may choose enter a long position near the trendline and then extend it into the future. If the price action breaches the trendline on the downside, the trader can use that as a signal to close the position. This allows the trader to exit when the trend they are following starts to weaken.
Trendlines are, of course, a product of the time period. In the example above, a trader doesn't need to redraw the trendline very often. On a time scale of minutes, however, trendlines and trades may need to be readjusted frequently.
Limitations of a Trendline
Trendlines have limitations shared by all charting tools in that they have to be readjusted as more price data comes in. A trendline will sometimes last for a long time, but eventually the price action will deviate enough that it needs to be updated. Moreover, traders often choose different data points to connect. For example, some traders will use the lowest lows, while others may only use the lowest closing prices for a period. Last, trendlines applied on smaller timeframes can be volume sensitive. A trendline formed on low volume may easily be broken as volume picks up throughout a session.
What Are the Different Kinds of Trendlines?
There are a number of different kinds of trendlines. The most common are characterized as linear, logarithmic, polynomial, power, exponential, and moving average.
What Is a Trendline?
Trendlines are easily recognizable lines that traders draw on charts to connect a series of prices together or show some data's best fit. The resulting line is then used to give the trader a good idea of the direction in which an investment's value might move.
A trendline is a line drawn over pivot highs or under pivot lows to show the prevailing direction of price. Trendlines are a visual representation of support and resistance in any time frame. They show direction and speed of price, and also describe patterns during periods of price contraction.
Example Using a Trendline
Trendlines are relatively easy to use. A trader simply has to chart the price data normally, using open, close, high and low. Below is data for the Russell 2000 in a candlestick chart with the trendline applied to three session lows over a two month period.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dotdash_Final_Trendline_Nov_2020-01-53566150cb3345a997d9c2d2ef32b5bd.jpg)
The trendline shows the uptrend in the Russell 2000 and can be thought of as support when entering a position. In this case, trader may choose enter a long position near the trendline and then extend it into the future. If the price action breaches the trendline on the downside, the trader can use that as a signal to close the position. This allows the trader to exit when the trend they are following starts to weaken.
Trendlines are, of course, a product of the time period. In the example above, a trader doesn't need to redraw the trendline very often. On a time scale of minutes, however, trendlines and trades may need to be readjusted frequently.
Limitations of a Trendline
Trendlines have limitations shared by all charting tools in that they have to be readjusted as more price data comes in. A trendline will sometimes last for a long time, but eventually the price action will deviate enough that it needs to be updated. Moreover, traders often choose different data points to connect. For example, some traders will use the lowest lows, while others may only use the lowest closing prices for a period. Last, trendlines applied on smaller timeframes can be volume sensitive. A trendline formed on low volume may easily be broken as volume picks up throughout a session.
What Are the Different Kinds of Trendlines?
There are a number of different kinds of trendlines. The most common are characterized as linear, logarithmic, polynomial, power, exponential, and moving average.



تبصرہ
Расширенный режим Обычный режим